Are you searching for reliable information about Alzheimer’s Disease? You’re not alone. Alzheimer’s is a common, progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory, thinking skills, and eventually, the ability to carry out the simplest tasks. It is the most common cause of dementia, a term for the decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with daily life.
Because it affects millions of seniors in the US and globally, understanding Alzheimer’s—its warning signs, what causes it, and how it is treated—is crucial. This article provides a clear, easy-to-understand guide to this serious neurological condition.
The Early Warning Signs of Alzheimer’s Disease
Many people confuse normal aging with Alzheimer’s. Occasional forgetfulness is normal, but the signs of Alzheimer’s Disease are more persistent and disruptive.
If you notice any of these symptoms in yourself or a loved one, it is time to consult a doctor:
| Key Warning Signs | Description |
| Memory Loss that Disrupts Life | Forgetting recently learned information, important dates, or repeating the same questions. |
| Challenges in Planning or Solving Problems | Difficulty following a familiar recipe or managing monthly bills. |
| Difficulty Completing Familiar Tasks | Struggling to drive to a familiar location or forgetting the rules of a favorite game. |
| Confusion with Time or Place | Forgetting where they are or how they got there, or being confused about the time of day. |
| New Problems with Words (Speaking or Writing) | Struggling to find the right word or calling things by the wrong name. |
| Misplacing Things | Putting items in unusual places (like keys in the freezer) and being unable to retrace steps. |
| Changes in Mood and Personality | Becoming confused, suspicious, depressed, fearful, or easily upset, often in simple situations. |
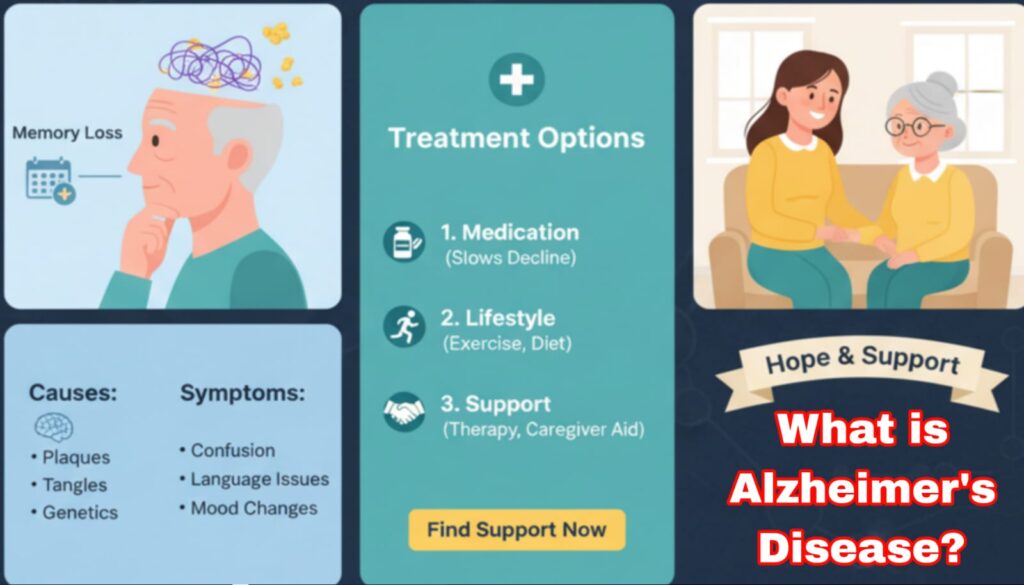
What Exactly Causes Alzheimer’s Disease?
The exact, single cause of Alzheimer’s is not fully understood, but scientists believe it results from a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
Struggling with Drugs? Find Top-Rated American Rehab Centers for Opioid and Fentanyl Addiction Now
The disease is characterized by two main physical changes in the brain:
- Plaques (Amyloid Beta): Abnormal clumps of a protein called beta-amyloid build up between brain nerve cells (neurons), disrupting cell function.
- Tangles (Tau Protein): Twisted fibers of a protein called Tau build up inside the neurons. These tangles block the transport system of the neurons, which stops essential nutrients from reaching the cells, eventually killing them.
These changes begin years before symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease even appear.
The Latest Treatment and Management Options
Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s Disease. However, treatments are available that can temporarily slow the worsening of dementia symptoms and improve the quality of life for both patients and caregivers.
1. Medication (Drugs to Manage Symptoms)
The primary goal of medication is to boost levels of communication chemicals in the brain.
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors: These drugs (like donepezil) are used to treat memory loss and are usually prescribed for mild to moderate Alzheimer’s.
- Memantine: This drug helps improve memory, attention, and reasoning and is used for moderate to severe stages of the Disease.
- Disease-Modifying Therapies (New Drugs): Recent FDA-approved drugs target the underlying cause by aiming to reduce the amyloid plaques in the brain (e.g., Aducanumab and Lecanemab). These are generally for early-stage patients.
2. Lifestyle and Supportive Care
Managing daily life and maintaining a healthy routine is just as important as medication.
- Cognitive Stimulation: Engaging in puzzles, reading, and listening to music can help maintain cognitive function for as long as possible.
- Physical Activity: Regular, moderate exercise is proven to help improve mood and sleep, which are often affected by the Disease.
- Safe Environment: Creating a safe, structured, and calm home environment helps reduce confusion and anxiety.
Conclusion: Hope and Support for Alzheimer’s Disease.
Living with or caring for someone with Alzheimer’s Disease is challenging, but support is available. Early diagnosis is key to starting treatment and planning for the future. If you are concerned about memory loss, talk to your primary care doctor or a specialist like a neurologist.
By staying informed and seeking appropriate medical guidance, the impact of Alzheimer’s can be managed, and the quality of life for those affected can be maintained.
